What is a granuloma?
A granuloma is a histological term for a collection of histiocytes or epithelioid histiocytes accompanied by a range of multinucleated giant cells (masses of macrophages) and another inflammatory cells [1].
What is a foreign body?
A foreign body is any material, living or non-living, that is recognized by host immunity to being 'not his own' and causes a immune reply.
What is a foreign body granuloma?
A foreign body granuloma forms in response to the introduction of exogenous material to the skin, or in response to modifications endogenous material that the immune system identifies as foreign [3].
Foreign body granulomas
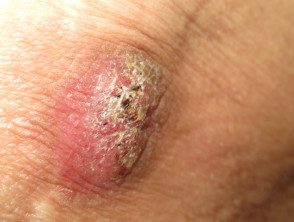
Silica granuloma
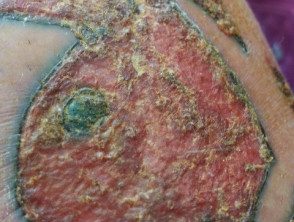
Granuloma tattoo
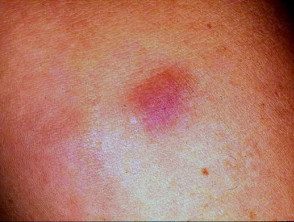
Bovine collagen granuloma
How does the body usually get rid of foreign bodies?
The body mounts an inflammatory reaction to get rid of foreign bodies. Neutrophils form the host's initial defense by trying to wrap and digest (engulf) the foreign material. If this response is not enough to remove the foreign body, then monocytes and local tissue macrophages will activate to gobble up the foreign material. If the foreign body is small enough, these cells will effectively remove it from the tissue [1–3].
If there are foreign bodies on the surface of the skin (like debris in a wound), keratinocytes migrate along the connective tissue formed by fibrin, fibronectin and type V collagenand dissect it from the underlying tissue during the proliferative healing phase.
Who receives a foreign body? granulomas?
Foreign bodies are most commonly introduced into the body through voluntary means, such as tattoos and cosmetic fillers. Unintentional causes of foreign body granulomas, such as minerals and metals accidentally embedded in the skin, are often seen in those who work in the construction industries [3].
What causes foreign body granulomas?
A foreign body granuloma forms when the host's immune system is unable to digest the foreign body, resulting in the accumulation of macrophages and histiocytes. As macrophages surround and isolate the foreign body, some of them will fuse to form multinucleated giant cells. T cells and fibroblasts it also participates in this inflammatory response [3].
Substances that cause foreign body granulomas include:
- Carbon pigments in cosmetic tattoos and industrial and firearm accidents.
- Cosmetic fillers, such as collagen, silicone, paraffin and hyaluronic acid.
- Medications, such as intralesional corticosteroids, polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP), and hydroquinone.
- Mineral and metallic particles, such as gravel, silica, aluminum, zinc and nickel.
- Broken cysthairs calcium
- Other biotic and abiotic materials, such as talc, cactus spines, glass, retained sutures, chips, and natural and artificial materials. hair.
What are the clinical features of foreign body granuloma?
Foreign body granulomas most commonly appear as red or red-brown papules, nodules or plates, which may or may not ulcerate [2,3].
Common presentations of foreign body granuloma.
Tattoos
Tattoo granulomas are usually limited to the tattoo area. Most often they are cute erythematous nodules Lichenoid or eczematous Plaques can also occur. Granulomas usually arise after a new tattoo, although late reactions have been reported up to 17 years after tattoo placement.
Bovine collagen injections
Hypersensitivity reactions to bovine collagen result in hardening and erythema in the area where the collagen was injected. Sterile abscesses can occur, which can last for several months or more.
Silicone implants and injections.
Silicone granulomas can form on the dermis when trauma causes the capsule around a silicone implant to break. Larger nodules, ulcers and sclerosis It can develop slowly, months or years after the injury. Distant nodules can also form due to silicone leakage in dependent sites.
Subcutaneous Liquid silicone injections can also cause cutaneous nodules and indurated or ulcerated plaques.
Paraffin injection
Paraffin injection for breast or penile implants can lead to firm, non-sensitive, nodule, an indurated and ulcerated license plate, and a abscess at the injection site. This reaction is known as a sclerosing lipogranuloma or oleogranuloma.
Intralesional corticosteroid injections.
A nodule may form at the site of intralesional corticosteroid injection due to incomplete absorption or unusual dispersion of the injected material.
Silica
Papules, nodules, and indurated plaques can develop within a scar after trauma involving glass, sand and dirt.
Aluminum
Aluminum can be introduced into the body through vaccines and immunotherapy. Granulomas may appear as persistent subcutaneous nodules a few months after injection.
Zinc
Granulomas are a rare side effect of insulin injections containing zinc. They present as sterile boils (boils), which then heal with atrophic scars at the injection site.
talcum powder
Talc (hydrated magnesium silicate) is found in many antibiotics and powder powders and can cause granulomas if these powders are applied to open wounds. Talc granulomas are erythematous papules or nodules that can take years to appear. Reported sites include the belly button infant, amputation stumps, injection sites and the inguinal zone.
Sutures
The retained suture material may be responsible for an inflamed wound a few weeks after a cutaneous surgical procedure. A fistula the surface of the skin can be formed, and the suture can be expelled from the skin (spit sutures). Natural materials, such as the intestine, are more likely to "spit" than nylon monofilament.
Cactus thorns
Cactus thorns can induce a acute inflammatory reaction and produces clusters of skin-colored domed papules, each with a black dot in the center. These are found on the hands and fingers of people who handle cactus fruit. A similar reaction can affect people who handle sea urchins.
What are the complications of foreign body granuloma?
Complications of foreign body granuloma can include:
- Ulceration and abscess formation
- Lymphadenopathy, due to the migration of the foreign body to lymphatic system
-
Keloids and hypertrophic scars, most commonly seen in individuals with dark skin [2,3].
How is a foreign body granuloma diagnosed?
Medical history and examination are often adequate to diagnose foreign body granuloma. Investigations may include:
- Biopsy and histological examination
- Ultrasound, especially in those with cosmetic fillers where biopsy is not desirable
- Observation of silica crystals under polarized light.
- Optical coherence tomography and confocal examination. To be microscopy of tattoos (eg, for evaluation before laser extraction) [2–4].
Which is the differential diagnosis for foreign body granuloma?
The differential diagnosis of foreign body granulomas includes other forms of granuloma and other foreign body reactions (for example, growing hairs can cause pseudofolliculitis, especially in the beard area). Differential diagnoses include:
- Skin sarcoidosis
- Granuloma annulare
- Pyogenic granuloma
- Facial granuloma
- Granulomatous dermatitis
- Actinic granuloma
- Inguinal granuloma
-
Majocchi granuloma [3–5].
What is the treatment for foreign body granuloma?
Foreign body granulomas can be removed. Other methods of removal depend on the cause.
Tattoos
Non-ablative (Q) quality lasers are the gold standard for superficial tattoo removal from the skin. Picosecond lasers have also been used. Surgical removal of deeper tattoo granulomas may be necessary.
Current Steroids, intralesional steroid injections, tacrolimus, imiquimod, and etanercept have been used successfully to treat granulomatous tattoo reactions.
Cosmetic fillers
Foreign body granulomas due to cosmetic fillers can be treated with antibiotics, oral steroids and
intralesional corticosteroid injections. Fluorouracil injections have also been used. Surgical removal can be carried out if other treatment options fail.
Other
Other medical options used to treat foreign body granulomas include:
- Colchicine
- Alopurinol
- Ascomycin
- Isotretinoin
What is the result of foreign body granuloma?
The natural history of foreign body granuloma varies by cause. Granulomas and foreign body abscesses due to bovine collagen injections often spontaneously regress in 1 to 2 years. [2–4]. Other types of foreign body granuloma can persist for decades.


