What is Sturge-Weber? syndrome?
Sturge-Weber syndrome is rare, congenitaland not inherited vascular disorder characterized by capillary malformation on the facial skin (port wine stain) and capillaryvenous malformations of the brain and eyes [1].
Sturge-Weber syndrome
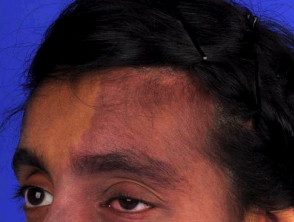
Sturge-Weber syndrome
Who gets Sturge-Weber syndrome?
It is estimated that approximately one in 20 to 50,000 babies are born with Sturge-Weber syndrome [2]. How is caused by a mosaic mutation, is not inherited from parents.
What causes Sturge-Weber syndrome?
Sturge-Weber syndrome is caused by a somatic mosaic mutation of the GNAQ gene in chromosome 9 9 [3]. This means that the mutation in the gene has occurred in the cells of the body after the formation of the zygote. GNAQ regulates intracellular signaling pathways. The mutation results in the uncontrolled formation or maturation of capillaries in the affected cells
What are the clinical features of Sturge-Weber syndrome?
Sturge-Weber syndrome is characterized by vascular malformations in the face and brain of affected people.
- Port wine stains are the most common type of vascular malformation, affecting approximately three out of every 1,000 babies, but most are not associated with Sturge-Weber syndrome [4].
- Port wine stains in Sturge-Weber syndrome are usually in the distribution of the first and second division of the trigeminal nerve in the forehead and upper eyelid [5]. They can also affect both sides of the face. [6].
- Leptomeningeal vascular malformations arise within the brain on the same side as the port wine stain.
- Leptomeningeal malformations can also occur without a port wine stain [7].
Other features of Sturge-Weber syndrome may include:
- Seizures and epilepsy
- Hemiparesis and stroke-like events
- Behavior problems
- Visual field defects and glaucoma
- Growth hormone deficiency.
What are the complications of Sturge-Weber syndrome?
The complications of Sturge-Weber syndrome depend on the extent of vascular malformations and other clinical features. They are extremely variable.
How is Sturge-Weber syndrome diagnosed?
The diagnosis of Sturge-Weber syndrome is based on finding port wine stains and leptomeningeal venous capillary malformations. A diagnosis based only on leptomeningeal lesions depends on the development of symptoms.
Yes there are neurological symptoms or findings, magnetic resonance image (Magnetic resonance) of the brain is performed with gadolinium contrast to detect capillary-venous leptomeningeal malformations.
Which is the differential diagnosis for Sturge-Weber syndrome?
The characteristics of other vascular malformation syndromes are described below.
-
Klippel-Trénaunay syndrome has more extensive capillary malformations, affects the extremities and trunk, and is associated with hypertrophy of the affected limb.
- Parkes-Weber syndrome presents with a large capillary malformation in one limb and hypertrophy of the affected limb. There are multiple fast-flowing arteriovenous shunts.
- Servelle-Martorell syndrome, a rare congenital angiodysplastic disease, is associated with progressive limb hypotrophy.
-
Proteus syndrome presents with asymmetric and disproportionate overgrowth of body parts. The syndrome results from a somatic activating mutation in the AKT1 oncogene.
-
CLOVES syndrome presents with congenital lipomatous overgrowth, vascular malformation, epidermal nevus, spinal / skeletal abnormalities /scoliosis. The syndrome results from the activation of the somatic mosaic. mutations at PIK3CA gene.
What is the treatment for Sturge-Weber syndrome?
There is no specific treatment for Sturge-Weber syndrome. Depends on managing the cutaneousneurological and ocular symptoms, with limited success.
Treatment of seizures in patients with Sturge-Weber syndrome with antiepileptics is not always successful [8]. No individual treatment seems to be higher to others.
Port wine stains can be treated with pulsed staining To be. Injuries to the face and neck produce worse results than injuries to other parts of the body. [9].
Glaucoma in patients with Sturge-Weber syndrome is treated surgically and medically [10].
Babies diagnosed with Sturge-Weber syndrome should be treated with low-dose aspirin [11,12]. Antithrombotic therapy can prevent the progression of the disease, which can affect blood flow to the brain and cause neuronal damage.
What is the result of Sturge-Weber syndrome?
the forecast Sturge-Weber syndrome depends on the degree of involvement of the brain and skin. Large port wine stains are associated with an increased risk of epilepsy and glaucoma, while bilateral Leptomeningeal vascular malformations are associated with learning and intellectual disability. [13]. The onset of seizures before the age of one year has a significant effect on cognitive and motor function in children with Sturge-Weber syndrome [14].
About one in two adults with Sturge-Weber syndrome is estimated to have neurological defects, even in those who were initially asymptomatic.

